Development of Polycentric Economies
Introduction
|
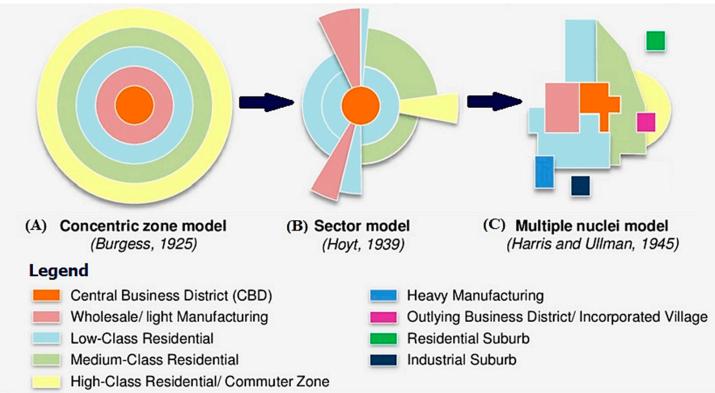
The traditional metropolis with a central business district surrounded by a ring of decreasing population density is no longer sustainable. As we approach the new standard of urban population density, which is a city with more than 10-15 million people, the most suitable cities of the future are being developed according to a multi-nodal, polycentric model (see Figure 1). |
|
What is a polycentric city? As the name suggests, it is a city with multiple centers, usually with one main center and several sub-centers.
|
|
Figure 1: City Structure The concept of polycentric cities provides better opportunities for creating a sustainable future for millions of people moving to cities in the coming decades. They should be built based on well-planned transport infrastructure, extensive public spaces, and multifunctional complexes for work, housing, and leisure.
This concept is not new. For example, downtown New York emerged through various constructions before it included surrounding areas such as the Bronx, Queens, Brooklyn, and Staten Island. London has been almost multi-centered since its inception. However, today we see that the center of gravity of new urban clusters in these cities is shifting.
Reasons for City Concentration Economists highlight two types of explanations for such concentration: «First-nature geography» and «Second-nature geography». First-nature geography is based on exogenous natural advantages or locations, such as access to natural water bodies or proximity to deep-water natural ports. Second-nature geography refers to the location of economic actors relative to each other in geographic space. Factors Affecting the Organization of Economic Activity in Polycenters According to economists, several factors affect the organization of economic activity in polycenters. |
Land Prices
Land prices are determined by competition between alternative types of land use and provide generalized statistics about the relative attractiveness of a region. The rise in land prices in some areas compared to others can be explained by demand for commercial or residential real estate.
Population Density
Differences in land prices are accompanied by significant differences in population density. Population density is also influenced by productivity and convenience.
Workers and Residents
Workers, when commuting to work, separate their place of residence and work to take advantage of high wages at the workplace and low living costs excluding utilities and housing costs at the residence.
Role of Government Institutions
In the context of global urbanization and rapid urban population growth, the creation of polycentric cities is becoming one of the key strategies for ensuring sustainable development.