Installation of Noise Radars in Almaty
Introduction
Since 1972, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized noise as a pollutant. In recent decades, the attention of researchers to urban environment quality has significantly increased due to the rapid growth of cities, especially in developing countries.
Reference: Noise pollution is defined as the repeated exposure to excessive sound levels that can harm humans or other living organisms.
According to the World Health Organization, noise levels under 70 decibels are not harmful to living beings, regardless of duration and regularity. Continuous noise above 85 decibels for more than 8 hours can be harmful. People who work or live near busy roads or highways for 8 hours a day are likely to be exposed to transport noise at around 85 decibels (Environmental Pollution Centers, 2022).
Noise pollution negatively impacts the lives of millions of people. Studies have shown a direct link between noise and health. Problems related to noise include stress-induced diseases, high blood pressure, speech disorders, hearing loss, sleep disturbances, and reduced productivity. Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is the most common and often discussed health effect, but studies have shown that exposure to constant or high levels of noise can cause countless negative health consequences. In France, a study by the National Noise Council and the French Agency for Ecological Transition showed that the annual cost of noise in terms of healthcare expenses amounts to 156 billion euros.
Below are the causes and sources of noise pollution (see Figure 1):
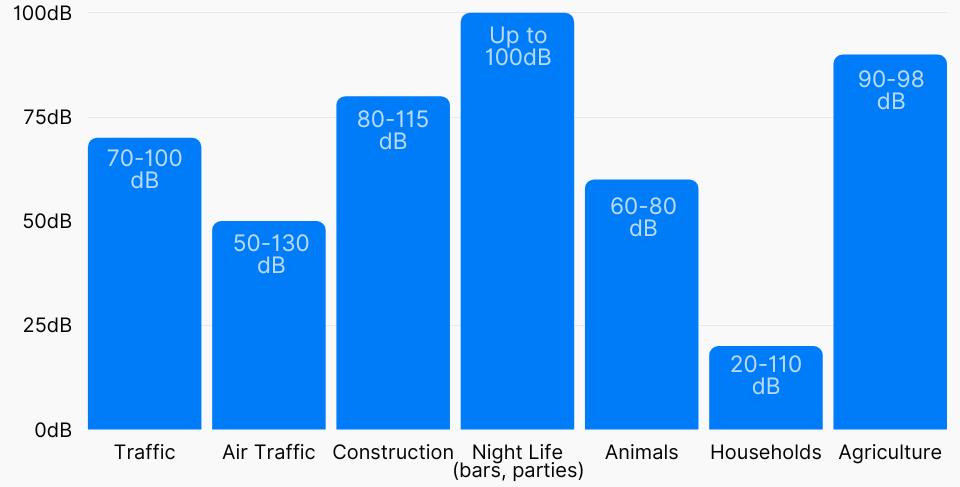 •
•
Figure 1. The most common sources of noise pollution
Industrialization: Industrialization has led to an increase in noise pollution due to the use of heavy equipment such as generators, mills, and large exhaust fans, which produce undesirable noise.
-
Vehicles: The increasing number of cars on the roads
is the second most significant cause of noise pollution.
-
Events: Weddings and public gatherings using loudspeakers to play music create undesirable noise in the neighborhood.
-
Construction sites: Mining, building construction, and other construction activities increase noise pollution.
Current Situation
Almaty, like many other megacities worldwide, has faced the problem of rapid growth in the number of cars, mopeds, and motorcycles in recent decades. This causes several negative consequences, including road congestion, air pollution, noise, parking shortages, and a decrease in the quality of life for city residents. Over the past two years, the number of registered cars in Almaty has increased by 24%, and by 2030, this figure may reach 40%.
Cars generate significant noise levels, which are exacerbated by the frequent and inappropriate use of horns by drivers. Moreover, the large number of mopeds with noisy exhaust systems creates considerable acoustic discomfort for residents and pedestrians.
Currently, the problem of noise pollution in Almaty is not regarded as serious, as evidenced by the lack of necessary equipment for measuring noise levels. Furthermore, vehicle inspections do not assess noise levels, unlike practices in other countries where such measures have already been implemented.
International Experience
In many cities around the world, noise pollution is considered one of the acute problems, and steps have already been taken to combat it. Special methods for reducing noise pollution are used in France and Spain. In these countries, the primary method for checking noise emissions is conducting vehicle inspections for noise levels (see Table 1 in the appendix).
If a vehicle with a non-standard exhaust attempts to pass inspection, the result of the test will be a failure. However, cases have increased where drivers temporarily remove and replace noisy exhaust systems with standard ones for passing the test, only to re-install the noisy one after passing the inspection.
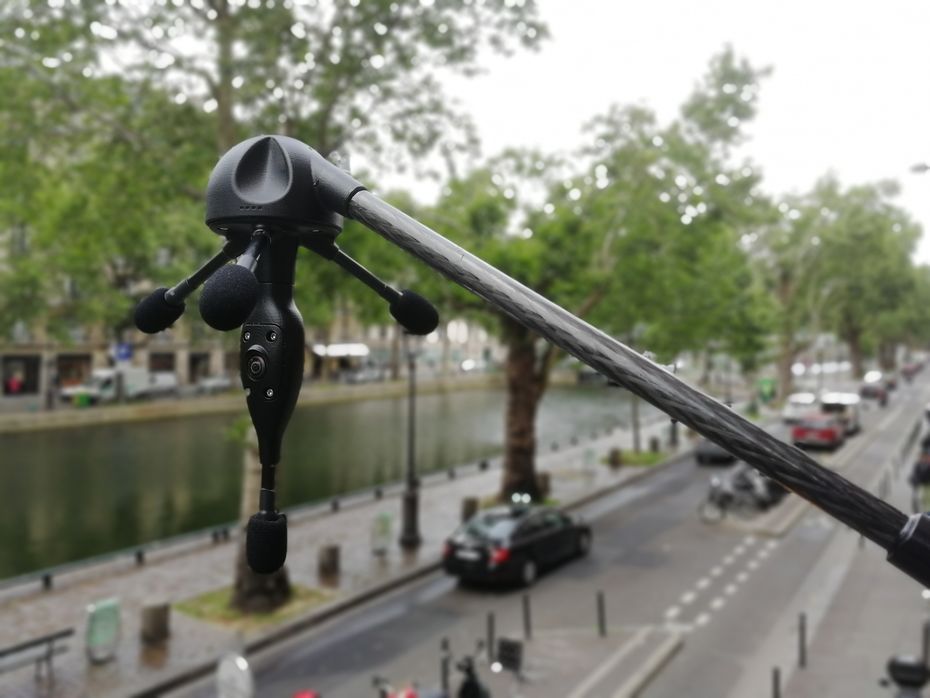
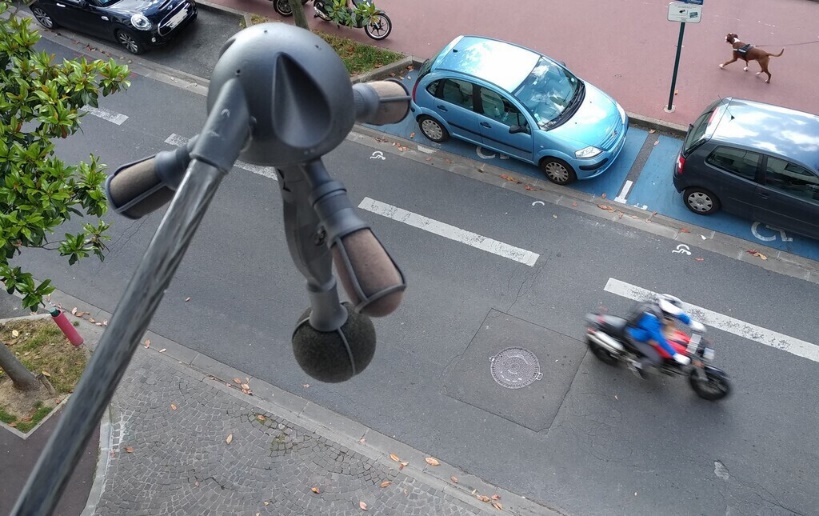
In this regard, some cities in France and Spain have started installing special radars, known as «Medusa Radars,» to detect noise violations on the streets of cities.
The device consists of three tentacles resembling the arms of a jellyfish (see Figure 2), hence its name. Each «arm" contains a high-precision microphone, and between them, there is a room and a 180-degree camera responsible for capturing vehicles emitting excessive noise.
|
|
|
Figure 2. «Medusa» Radar
In addition to the «Medusa» model, there are other radars of this type that work in a similar way: they detect noise and photograph the license plates of violating vehicles. In 2021, France launched a pilot project for the installation of such radars at eight locations. These devices also appeared in Spain in 2022. In France, the radars detect and fine the owners of the noisiest cars with a fine of 135 euros, while in Spain, the «Medusa» radars are only used for noise detection.
Recommendations
The provided information shows that noise pollution is becoming an increasingly significant issue in megacities, including Almaty. To reduce and control the negative impact of noise on the city's residents, the following recommendations can be proposed:
Implementation of noise level assessments during vehicle inspections: Conducting vehicle inspections with noise level evaluations, as practiced in many other countries, will help identify and fine vehicles that exceed the permissible noise levels.
Installation of specialized radars: Implementing special radars, similar to the «Medusa Radars» in France and Spain, to automatically detect and record noise violations on the streets.
Public education and awareness: Conducting educational campaigns and informing the public about the harm of noise pollution, its health consequences, and methods of noise reduction.
Regulating traffic flow: Introducing measures to reduce the number of noisy vehicles, such as encouraging the use of quiet electric cars or limiting the hours of operation for noisy events.
Infrastructure changes: Developing and implementing urban zoning to reduce noise loads in residential areas, as well as improving road infrastructure to reduce noise from traffic.
Implementing these measures will enable Almaty to effectively address the problem of noise pollution and improve the quality of life for its residents.
Appendix
Table 1. Spanish vehicle suitability test for noise
|
Type of defect |
Cause of defect |
|
Vehicle identification |
Documentation, VIN Number, Number plates |
|
Exterior condition, body and chassis |
Front anti-roll device, Body and chassis, Towing devices (tow bar), Mudguards and splash devices, Windshield wipers and washers, Side protection, Rear protection, Doors and steps, Mirrors, Vehicle signs, External spare wheel holder, Protective glass |
|
Interior condition |
Seats and their fastenings, Seat belts and their fastenings, Child restraint device, Defroster and fog lights, Anti-theft devices and alarms, Direct visibility, Cargo retention devices, Speed indicator (odometer), Internal protrusions. |
|
Lighting and signaling |
Low and high beam, reverse lights, signal lights (turn signals), emergency signals, brake lights, rear license plate light, side lights, fog lights, marker lights, reflectors, internal lighting, acoustic warning, parking light, door opening warning, specific light signal |
|
Pollutants and noise |
Pollutants, noise |
|
Brakes |
Working brake, Secondary (emergency) brake, Parking brake (handbrake), Overtaking brake, Anti-lock device, Slowing device, Brake pedal, Vacuum pump or compressor and tanks, Low pressure indicator, Handbrake regulating valve, Brake valves, Battery or pressure tank, Trailer brake connection, Brake booster, Master cylinder (hydraulic systems), Rigid tubes, Flexible tubes, Gaskets, Drums and/or discs, Cables, rods, levers, joints, Brake cylinders, Load sensor valve, Automatic slack adjusters |
|
Steering and direction |
Wheel deviation, Steering wheel and column, Steering mechanism, Steering wheel and ball joints, Power steering |
|
Axles, wheels, tires, and suspension |
Axles, wheels, tires, suspension |
|
Engine and transmission |
Engine general condition, Administration, Exhaust system, Transmission, Vehicles using gas (LPG) as fuel |
|
Other |
Transporting hazardous goods, School and small transport, Tachograph, Speed limiter, Unauthorized changes or modifications |














